Hair transplant procedures aim to restore hair. They can, however, leave some scarring. Patients should know what to expect. Scars are a natural part of healing. Their appearance varies greatly. It depends on several factors. Knowing these helps manage expectations. Discussing this with your surgeon is vital. Transparency from the start is important. Every case is unique.
Hair Transplant Scarring: What to Expect
Scarring is an important consideration. It is part of any surgical process. Hair transplants are no exception. Different techniques yield different scars. Understanding these differences is key. This helps in making informed decisions. Your surgeon will explain everything. Prepare for potential outcomes. Individual healing varies.
FUT Scars: A Linear Mark
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) involves a strip. A piece of scalp is removed. This leaves a linear scar. The scar is typically at the back. It can be long and narrow. Its visibility depends on hair length. Shorter hair makes it more noticeable. Good closure techniques minimize its appearance. Some people hide it easily. Others find it challenging.
Factors Affecting FUT Scar Visibility
Many factors influence FUT scars. The surgeon’s skill is crucial. Patient skin elasticity plays a role. Wound healing varies among individuals. Proper post-operative care helps. Avoid tension on the scar line. Certain activities can stretch it. Discuss all risks with your doctor. Genetic predispositions also matter. Recovery is a journey.
FUE Scars: Dot-Like Marks
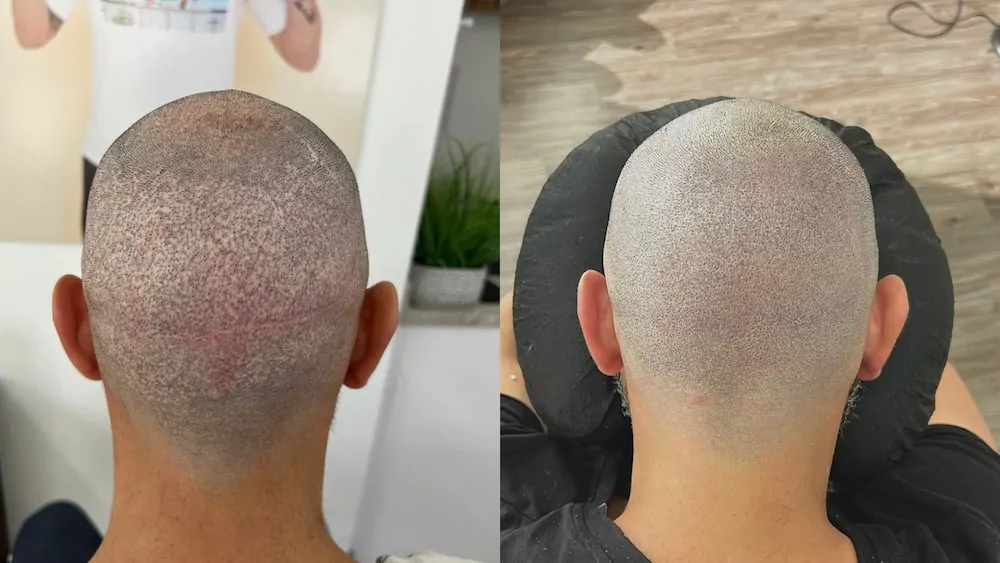
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) is different. Individual follicles are extracted. This creates tiny dot-like scars. They are scattered across the donor area. These dots are usually very small. They are often less noticeable. Shaving the head can reveal them. They are generally discreet with short hair. Some prefer this method. It offers more styling freedom.
Minimizing FUE Scarring
Minimizing FUE scarring is possible. Experienced surgeons use smaller punches. This reduces scar size. Proper technique prevents over-harvesting. Over-harvesting can thin the donor area. It can make scars more prominent. Patient hair characteristics also matter. Discuss your hair type with the clinic. Donor density is also key. Not everyone is an ideal candidate.
Recipient Area Scarring
Scarring can also occur in recipient areas. Tiny incisions are made there. These create sites for new grafts. These usually heal quickly. They are typically unnoticeable once hair grows. Folliculitis can sometimes occur. This is inflammation of the follicles. It can impact healing. Redness might linger for weeks. Patience is required for full results.
Managing Existing Scars
Existing scars can be improved. Several options are available today. Scalp micropigmentation (SMP) is one. It can camouflage scars effectively. Laser treatments might reduce redness. Scar revision surgery is another option. Discuss possibilities with a specialist. They can advise on the best approach. Each method has pros and cons. Personalized plans work best.
Patient Factors in Scarring
Patient-specific factors influence scarring. Age can impact healing. Younger skin often heals better. Smoking can hinder recovery. Underlying health conditions are also important. Diabetes can affect wound closure. Always provide a full medical history. This helps anticipate healing. Nutritional status is also vital. A healthy body heals better.
Long-Term Scar Evolution
Scars evolve over time. They may appear red initially. This fades as they mature. It can take many months for full maturation. Some scars might stretch. Others may remain quite subtle. Protecting scars from sun is important. Sun exposure can darken them. Ongoing care improves the outcome. Regular check-ups are helpful.
Understanding hair transplant scarring is vital for realistic expectations and informed decisions, ensuring a smoother journey to restoration.